Pros and Cons of Vegetarian Diet
Know these pros and cons of Vegetarian Diet .Although it may help you lose weight and boost your health .But the diet is not right for everyone .
Many people go vegetarian to improve their health or reduce their risk of developing the disease. Of course, the benefits of a plant-based diet are well documented. But not all vegetarian diets are nutritious.
The type of foods you choose in your diet plan (and those you choose to avoid) are very different from the benefits you get. A vegetarian diet that is all processed foods is less likely to provide health benefits than a diet full of nutritious fruits, vegetables, legumes, and grains.
When you consider adopting this diet plan, consider all the pros and cons of a vegetarian diet to make sure it’s right for you.
There are many different types of vegetarian food. The most common are lacto-egg vegetarians, or people who avoid meat, poultry, and seafood but consume dairy and eggs. Ovo vegetarians eat eggs but avoid dairy, meat, and seafood. Lacto-vegetarians consume dairy products but avoid eggs, meats, and seafood. These can all provide a variety of benefits.
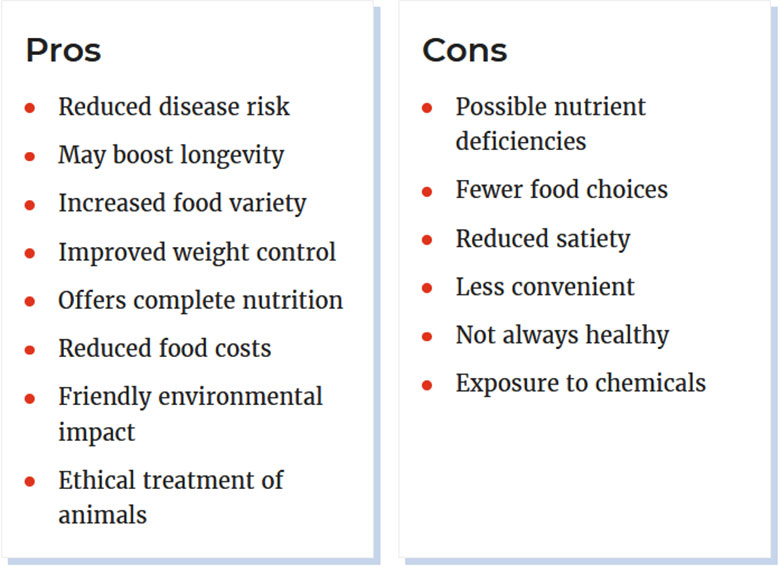
Pros
- Reduces the risk of disease
In a healthy vegetarian diet, you are encouraged to consume whole grains, legumes, fruits, vegetables, nuts, and seeds that are lacking in the diets of many people who follow more traditional food plans. These plant-based foods provide your body with important vitamins and minerals that promote your health and reduce the risk of many chronic diseases.
For example, in a large cohort study evaluating vegetarian and vegan diets, researchers found that both groups had a reduced risk of cardiovascular disease, cardiometabolic risk factors, and certain cancers.
There is also some evidence that a vegetarian diet can help you avoid diseases such as gallstones and kidney stones. A 2019 study published in the journal Nutrients followed more than 4,800 participants and concluded that by lowering cholesterol levels, a vegetarian diet successfully reduced the incidence of gallstone disease.
A 2014 study investigating the effects of various diets on kidney stone formation showed that a balanced lacto-ovo vegetarian diet could prevent this condition with adequate calcium intake.
- Can extend life sapn
There are many studies investigating the link between a vegetarian or vegan diet and longevity. Some studies have found that those who follow a healthy plant-based diet live longer than those who eat meat.
A large cohort study published in 2014 found that vegetarians were 12 percent less likely to die from all causes compared to non-Vichys.
However, the results of such studies may be difficult to interpret. The 2014 cohort study included 73,000 people, but they were all seventh-day adventurists who generally didn’t drink alcohol or smoke. 1 These factors may have played a role in their longevity patterns.
Other studies have investigated the link between a plant-based diet and longevity, and many studies have found a positive correlation. But it’s hard to tell whether it’s diet itself or a life-prolonging factor.
For example, people who choose a vegetarian or vegan diet often practice mindfulness eating, exercise regularly, and manage stress through meditation or yoga. These habits may also play a role in providing benefits.
- Increase the variety of food
The standard American diet is known as the omnivorous diet because no food is excluded. But more often than not, people who eat omnivorous diets eat the same foods day after day. The result is that the food or variety of foods they eat is relatively limited.
For example, a traditional American dinner typically includes meat (such as steak or pork chops), starchy side dishes (such as potatoes or rice), and perhaps vegetables. Dairy products are often used as ingredients, side dishes or ingredients.
However, on vegetarian diets, many traditional foods do not meet the requirements. So when you start this diet, you may need to creatively try unfamiliar foods. For example, in the absence of meat, lentils, beans, or peas may become the basis of your meals. Then to fill your plate, you can rely on a variety of vegetables.
Of course, choosing only a vegetarian diet does not guarantee this benefit. Vegetarians can also get into food dilemmas and eat the same (unhealthy) foods every day. But switching to a vegetarian diet may provide an incentive to try new, healthier food options.
- Improve weight control
A plant-based diet is often associated with weight loss. Studies have shown that those who follow a vegetarian diet typically consume fewer calories than an omnivorous diet. The researchers also found that the most restrictive changes in a vegetarian diet may also have the lowest calorie intake.
An extensive review of evidence published in 2017 found that a plant-based diet is an effective tool for managing and preventing overweight and obesity.
If you’re trying to reach or maintain a healthy weight, the lower daily calorie intake associated with vegetarian or vegan diet may help you achieve your goals.
- Provides complete nutrition
It is recommended that the intake of large and micronutrients is easier than that of vegetarians. While there are still some concerns about nutritional deficiencies in a vegetarian diet, there are still plenty of resources available to help you meet your nutritional needs.
For example, the U.S. Department of Agriculture and the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services have made healthy vegetarian eating patterns part of their dietary guidelines for Americans 2020-2025. Recommendations for eating various food categories such as green leafy vegetables, starchy vegetables, legumes and legumes, soy products, etc. are provided here.
Provides recommended amounts for daily calorie intake, with a daily calorie intake of 1,000 to 3,200 calories. By following this guide, you may be getting the daily vitamins, minerals, and macronutrients you need for a healthy body. However, like any diet, if you don’t take steps to eat a balanced diet, you may be deficient in nutrients.
- Reduce food costs
Choosing a vegetarian diet may help reduce food costs. But your total food cost will ultimately depend on the foods you choose to include in your meal plan.
Meat and seafood are often expensive, and for many people, this is a major component of their total food cost. Convenience foods and fast food that are not vegetarian can also be expensive. When you remove these foods from your diet, you can eliminate the large amount of food costs associated with them.
Bulk grains and legumes are generally budget-friendly. If you buy produce in season, you can also reduce costs. Of course, vegetarian convenience foods and meat substitutes can be expensive, but their overall cost may be lower than diets rich in animal-based products.
- Friendly environmental impact
The environmental community is increasingly concerned about the impact of livestock and livestock practices on the planet. So, some people choose to eat meat and eat vegetarian food because they feel it’s better for the planet.
Plants that grow fruits, vegetables, nuts, seeds, and grains require less land and water than producing meat, poultry, and dairy products. Cows produce more greenhouse gases than plants, which has led some to believe that eliminating meat and dairy products from their diets helps reduce the risk of global warming.
Some studies have even shown that vegetarian variants are better for the planet than other diets, including the popular Mediterranean diet.
- Ethical treatment of animals
Since no animals are killed to produce a vegetarian diet, many people choose this diet for fear of animal abuse. However, those who choose to consume eggs and dairy products may still have to face questions about the treatment of chickens and cows.
Animal rights activists prefer consumers to choose a vegetarian diet to promote ethical treatment of animals. But less restrictive vegetarian options can still reduce the overall impact on the animal population.

Cons
- Possible nutritional deficiencies
A comprehensive vegetarian diet can provide enough nutrition. However, if the diet does not include a variety of healthy foods, certain key nutrients that are often found in animal foods may be deficient in a vegetarian diet.
Zinc: Studies have shown that although vegetarians tend to have lower zinc intakes, their bodies adapt to lower levels by increasing the absorption and retention of minerals. The researchers also noted that a well-planned diet can provide enough zinc from plant sources such as whole grains, tofu, tempeh, legumes, nuts and seeds, fortified breakfast cereals, and dairy products.
Vitamin B-12: Vitamin B-12 or cobalamin is found in beef, liver, fish, shellfish, chicken, and other meats – foods that are not eaten when vegetarian. But eggs contain vitamin B12, as well as some fortified breakfast cereals and dairy products. However, researchers have found that people on vegetarian or vegan diets may need supplements.
Vitamin D: Some researchers and health experts have expressed concern about vitamin D levels in vegetarians and vegans. Vitamins occur naturally in fish, cod liver oil and egg yolks. But most of our vitamin D comes from exposure to sunlight. Two excellent vegetarian sources of vitamin D include maitake mushrooms and Portobleo mushrooms. Fortified nut milk and fortified grain products may help increase vitamin D intake during the winter months.
Calcium: Vegetarians who do not eat dairy products may need to carefully plan their meals to get enough calcium. But leafy greens, white beans, legumes, sesame seeds and some dried fruits are rich in nutrients. Many brand names of nut milk and orange juice also contain calcium.
Omega-3: Finally, a vegetarian diet may be deficient in omega-3 fatty acids. But soybean, pumpkin, flax or chia seeds and walnuts are good sources of omega-3.
It is important to read nutrition labels and choose foods that contain key vitamins and minerals to avoid nutrient deficiencies.
- Fewer food options
If you’re used to eating a traditional diet that includes meat, seafood, and other animal products, you may find that vegetarianism is limited in the first place. Of course, if you’re used to eating bacon for breakfast, cooked meat for lunch, and beef or chicken for dinner, it will take time to adjust to your eating habits.
But there are a variety of resources that can help you learn to find or create satisfying meals without meat. Most vegetarians find plenty of options not only in grocery stores and restaurants, but even when dining with friends and family in private homes. Health professionals often encourage plant-based dishes for meat eaters, so it’s not uncommon to see vegetarian-friendly heart-to-heart dishes.
- Decreased satiety
Studies have found that vegetarian diets tend to have lower calories, fats, and proteins than omnivorous diets. 10 Foods high in fat and protein can help you feel full and satisfied after eating.
Some carbohydrate-rich foods, such as fruits or refined grains, will be digested more quickly and may make you feel hungry soon after a meal or snack. Therefore, when you switch to a vegetarian diet, you may be more dissatisfied and hungry.
But careful food choices can help improve satiety. Hearty beans and whole grains are high in fiber to help you feel full. Snacks including nuts or seeds also provide protein and fat to increase post-eat satisfaction.
- Not very convenient
Although plant-based foods are becoming increasingly easy to find, those who follow a vegan diet still need to read the ingredient list, especially if they choose to eat processed foods. Foods that you might think of as not containing animal by-products may contain gelatin, whey, casein, or other non-compliant foods.
Eating out can also be a challenge, especially when you’re adjusting to a strict vegetarian diet for the first time. While some restaurants offer meatless meals, meals can be made with dairy products or other animal products. For example, vegetable soups can be made with chicken or beef soup, or even vegetable soups flavored with animal bones.
Eventually, you might find restaurants with plenty of compatible plant-based meal options. When dining at someone’s house, bring vegetarian recipes that you can enjoy and share with others.
- It’s not always healthy
While eating a vegetarian diet can provide health benefits and help you maintain a healthier weight, it’s not a guarantee. More and more heavily processed vegetarian foods. Many times, these foods contain more fat, sodium, added sugars, and calories than traditional foods.
Relying on these convenience foods can lead to the same limited food taste and health problems as the traditional American diet.
In fact, a study investigating vegan diets found that those who followed a diet that included whole grains, fruits, vegetables, nuts, legumes, oils, tea and coffee had a much lower risk of heart disease. But those who chose less healthy diets, including sugar-sweetened beverages, refined grains, potatoes, fries and sweets, were at higher risk.
- Exposure to chemicals
The health community has been concerned about the increased risk of exposure to herbicides and pesticides for people who consume plant-based diets.
In fact, some studies have shown that because fruits, vegetables, and grains are often farmed with these chemicals, vegetarians may be more exposed to pesticide residues than the general population due to specific eating habits. However, even though exposure to pesticides may be higher, other researchers have found that it is still possible to fall within safety guidelines.
In addition, it is unclear whether limited exposure is more harmful than exposure to hormones or antibiotics sometimes found in animal foods, or whether potential exposure reduces the benefits gained by eating a plant-based diet.
An easy way to solve this problem is to buy organic food. However, these products are often expensive and may not be available in all areas. If organic products are not suitable for you, health experts recommend that you carefully wash fruits and vegetables to limit exposure.




